Contents
- 1 ļŹ░ņØ┤Ēä░ ņĢĢņČĢņØś ĻĖ░ļ│ĖņĀüņØĖ ņé¼ĒĢŁ
- 2 ĒÄśņØ┤ņ¦Ć ņĢĢņČĢ ŌĆō column-prefix
- 3 ĒÄśņØ┤ņ¦Ć ņĢĢņČĢ ŌĆō data-dictionary
- 4 Overhead
- 5 ņśłņĀ£
- 6 ĒģīņØ┤ļĖö ļ░Å ņØĖļŹ▒ņŖż, ĒĢäĒä░ļ¦üļÉ£ ņØĖļŹ▒ņŖżņŚÉ ļīĆĒĢ£ ņĢĢņČĢ ņśłņĀ£
- 7 DBņØś ļ¬©ļōĀ ĒģīņØ┤ļĖö ļ░Å ņØĖļŹ▒ņŖż ņĢĢņČĢĒĢśĻĖ░
- 8 ņĢĢņČĢņŚ¼ļČĆ ņĪ░ĒÜī
- 9 ĒīīĒŗ░ņģś ņĢĢņČĢ
- 10 Ļ▓░ļĪĀ
- 11 ņ░ĖĻ│Āņ×ÉļŻī
SQL Server 2008ņŚÉ ņāłļĪŁĻ▓ī ņäĀļ│┤ņØĖ ĻĖ░ļŖźņØ┤ļŗż.
[edit]
1 ļŹ░ņØ┤Ēä░ ņĢĢņČĢņØś ĻĖ░ļ│ĖņĀüņØĖ ņé¼ĒĢŁ #
ļŹ░ņØ┤Ēä░ ņĢĢņČĢņØś ņóģļźśņÖĆ ņĀ£ĒĢ£ņé¼ĒĢŁ
2Ļ░£ņØś 16ņ¦äņłśļĪ£ Ēæ£ĒśäļÉ£ ļŹ░ņØ┤Ēä░ 0x020406FF, 0x0204CCFFĻ░Ć ņ׳ļŗż. ņŚ¼ĻĖ░ņä£ Common 'byte' patternņØĆ '0x0204'ņØ┤ļŗż. 4ļ▓łņ¦Ė byteĻ░Ć FFļĪ£ Ļ░ÖņØĆļŹ░, 3ļ▓łņ¦Ė byteĻ░Ć Ļ░üĻ░ü '06', 'CC'ņØ┤ļ»ĆļĪ£ ņØ┤ļŖö Common 'byte' pattern ņØ┤ ņĢäļŗłļŗż. ļ╣äņŖĘĒĢ£ ņśłļĪ£ 0xFFAABBCCDDEE ņÖĆ 0x33AABBCCDDEEĻ░Ć ņ׳ļŗż. ņØ┤ļŖö Common 'byte' patternņØ┤ ņĢäļŗłļŗż. ņÖ£ļāÉĒĢśļ®┤ Ļ░üĻ░ü 2~5ļ▓łņ¦Ė byteļŖö Ļ░Öņ¦Ćļ¦ī 1ļ▓łņ¦Ė byteĻ░Ć Ļ░üĻ░ü 'FF', '33'ņ£╝ļĪ£ ļŗżļź┤ĻĖ░ ļĢīļ¼ĖņØ┤ļŗż.
- Row Compression : intĒśĢ 3ņØĆ 4byteĻ░Ć ņĢäļŗī 1ļ░öņØ┤ĒŖĖļĪ£ ņĀĆņן
- Page Compression : Ļ░ÖņØĆ Ļ░ÆļōżņØĆ 1ĒÜīļ¦ī ņĀĆņן (column-prefix ņĢĢņČĢ Ēøä data dictionary ņĢĢņČĢ)
- ĒģīņØ┤ļĖöņŚÉ 2Ļ░£ ņØ┤ņāüņØś ņØĖļŹ▒ņŖżĻ░Ć ņĪ┤ņ×¼ĒĢśļ®┤ ņØĖļŹ▒ņŖżļ¦ī ņĢĢņČĢĒĢ£ļŗż.
- singleton LookupņØś Ļ▓ĮņÜ░ļŖö ņŗ¼ņé¼ņłÖĻ│Ā ĒĢ┤ņĢ╝ ĒĢ£ļŗż. (Compression/De-Compression ļ╣äņÜ®)
- DDL ņ¦ĆņøÉ(ņāłļĪ£ņÜ┤ Ēéżņøīļō£)
- XML, BLOB, MAX ļŹ░ņØ┤Ēä░ ĒśĢņŚÉļŖö ņé¼ņÜ®ļÉĀ ņłś ņŚåļŗż.
- Row CompressionņØĆ Vardecimal Storage Format ļÅä ņ░ĖĻ│Ā.
- 4ļ░öņØ┤ĒŖĖ ņ╗¼ļ¤╝, 1ļ░öņØ┤ĒŖĖ -> 1ļ░öņØ┤ĒŖĖļĪ£ ņĢĢņČĢ
- 1ļ░öņØ┤ĒŖĖ ņ╗¼ļ¤╝, 1ļ░öņØ┤ĒŖĖ -> 1ļ░öņØ┤ĒŖĖļĪ£ ņĢĢņČĢ
2Ļ░£ņØś 16ņ¦äņłśļĪ£ Ēæ£ĒśäļÉ£ ļŹ░ņØ┤Ēä░ 0x020406FF, 0x0204CCFFĻ░Ć ņ׳ļŗż. ņŚ¼ĻĖ░ņä£ Common 'byte' patternņØĆ '0x0204'ņØ┤ļŗż. 4ļ▓łņ¦Ė byteĻ░Ć FFļĪ£ Ļ░ÖņØĆļŹ░, 3ļ▓łņ¦Ė byteĻ░Ć Ļ░üĻ░ü '06', 'CC'ņØ┤ļ»ĆļĪ£ ņØ┤ļŖö Common 'byte' pattern ņØ┤ ņĢäļŗłļŗż. ļ╣äņŖĘĒĢ£ ņśłļĪ£ 0xFFAABBCCDDEE ņÖĆ 0x33AABBCCDDEEĻ░Ć ņ׳ļŗż. ņØ┤ļŖö Common 'byte' patternņØ┤ ņĢäļŗłļŗż. ņÖ£ļāÉĒĢśļ®┤ Ļ░üĻ░ü 2~5ļ▓łņ¦Ė byteļŖö Ļ░Öņ¦Ćļ¦ī 1ļ▓łņ¦Ė byteĻ░Ć Ļ░üĻ░ü 'FF', '33'ņ£╝ļĪ£ ļŗżļź┤ĻĖ░ ļĢīļ¼ĖņØ┤ļŗż.
[edit]
2 ĒÄśņØ┤ņ¦Ć ņĢĢņČĢ ŌĆō column-prefix #
SQL ServerļŖö ĒĢśļéśņØś column-prefix dataļź╝ ņāłļĪ£ņÜ┤ ļĀłņĮöļō£ļź╝ ņāØņä▒ĒĢ£ļŗż. ņØ┤ ļĀłņĮöļō£ļź╝ anchor-record ļØ╝Ļ│Ā ļČĆļźĖļŗż. Anchor-recodeļŖö ĒÄśņØ┤ņ¦Ć ĒŚżļŹö ļŗżņØīņŚÉ ņĀĆņןļÉ£ļŗż. ļ¦īņĢĮ Common ŌĆśbyteŌĆÖpattern ņØ┤ ļ░£Ļ▓¼ļÉśņ¦Ć ļ¬╗ĒĢśļ®┤ empty ļśÉļŖö nullļĪ£ ņĘ©ĻĖēļÉ£ļŗż. ļ¦īņĢĮ column-prefixļź╝ Ļ░Ćņ¦Ćņ¦Ć ņĢŖļŖöļŗżļ®┤ Anchor-recordļŖö ņāØņä▒ļÉśņ¦Ć ņĢŖļŖöļŗż. ļŗżņØīņØś ĻĘĖļ”╝Ļ│╝ Ļ░ÖņØ┤ ĒĢśļéśņØś ĒÄśņØ┤ņ¦ĆņŚÉ ļĀłņĮöļō£ļōżņØ┤ ņĀĆņןļÉśņ¢┤ ņ׳ļŗż.
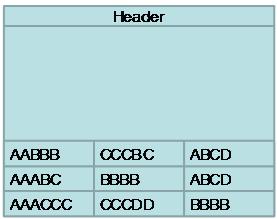
SQL ServerļŖö Ļ░üĻ░üņØś ņ╗¼ļ¤╝ņŚÉ ļīĆĒĢ£ ļĀłņĮöļō£ļź╝ ņØĮĻ│Ā, Common ŌĆśbyteŌĆÖpattern ļŻ░ņŚÉ ņØśĒĢ┤ņä£ Column-prefixļź╝ ņ░ŠļŖöļŗż.
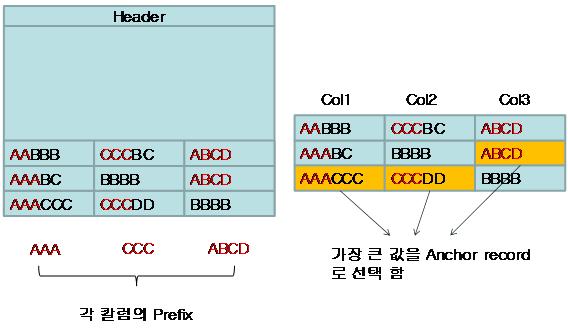
SQL ServerļŖö Page Header ļ░öļĪ£ ļŗżņØīņŚÉ Anchor-Recordļź╝ ļ¦īļōĀļŗż.
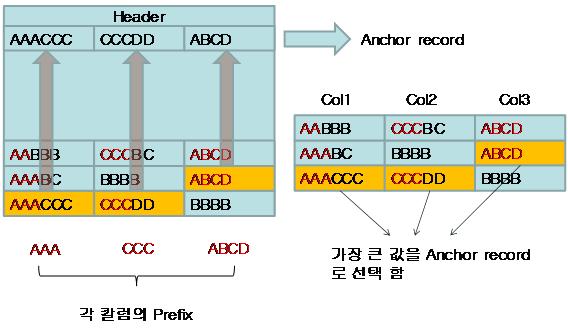
SQL ServerļŖö Anhcor recordļź╝ ļŗżļźĖ ļĀłņĮöļō£ļĪ£ ņĘ©ĻĖēĒĢ£ļŗż. ĻĘĖļ¤¼ļ»ĆļĪ£ SELECT ņ┐╝ļ”¼ļĪ£ ņĪ░ĒÜīĻ░Ć ļČłĻ░ĆļŖźĒĢśļŗż. SQL ServerļŖö Anchor-recordņŚÉ Column-prefixļ¦ī ņĀĆņןĒĢśņ¦Ć ņĢŖĻ│Ā, Ļ░Ćņן Ēü░ ļŹ░ņØ┤Ēä░ļź╝ ņĀĆņןĒĢ£ļŗż. ņÖ£ļāÉĒĢśļ®┤ ĻĘĖļלņĢ╝ļ¦ī ņĢĢņČĢĒĢĀ ņłś ņ׳ļŖö ļŹ░ņØ┤Ēä░ņØś ļ▓öņ£äĻ░Ć ļäōņ¢┤ņ¦ĆĻĖ░ ļĢīļ¼ĖņØ┤ļŗż. ļŗżņØīņØĆ ņØ┤ļ¤░ Ļ│╝ņĀĢņØä Ļ▒░ņ│Éņä£ ĒÄśņØ┤ņ¦ĆĻ░Ć ņĢĢņČĢļÉ£ Ļ▓░Ļ│╝ņØ┤ļŗż.
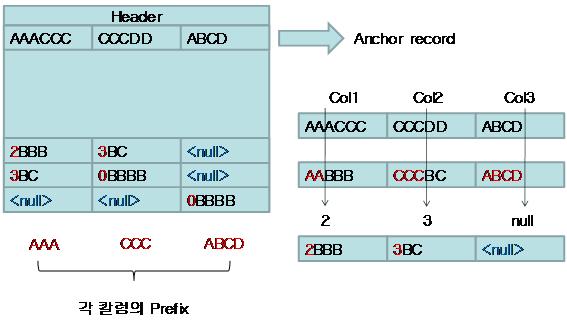
ĻĘĖļ”╝ņŚÉņä£ ņĢĢņČĢļÉ£ ļŹ░ņØ┤Ēä░ņØś Ēæ£ĒśäĒĢ£ŌĆś2BBBŌĆÖņØś ņØśļ»ĖļŖö Anchor record ņ▓½ ļ▓łņ¦Ė Column-prefix ņØĖ ŌĆśAAACCCŌĆÖņØś 1~2ļ▓łņ¦Ė byteĻ╣īņ¦ĆņØś ļŹ░ņØ┤Ēä░Ļ░Ć Ļ░ÖļŗżļŖö ņØśļ»ĖņØ┤ļŗż. ņśłļź╝ ļōżņ¢┤ ņ▓½ ļ▓łņ¦Ė ņ╗¼ļ¤╝ņŚÉ ļīĆĒĢ£ Anchor recordņØś ņ▓½ ļ▓łņ¦Ė ņ╗¼ļ¤╝ņØś Ļ░ÆņØ┤ ŌĆśAAAAAAAAAAAAAACCŌĆÖņØ╝ ļĢī ļĀłņĮöļō£ņØś Ļ░ÆņØ┤ ŌĆśAAAAAAAAAAAAAAŌĆÖļØ╝ļ®┤ 14ļĪ£ Ēæ£ĒśäĒĢśņŚ¼ ņĀüņ¢┤ļÅä 10byteņØ┤ņāüņØĆ ņżäņØ╝ ņłś ņ׳ļŗż.
[edit]
3 ĒÄśņØ┤ņ¦Ć ņĢĢņČĢ ŌĆō data-dictionary #
Data-dictionary ņĢĢņČĢļ░®ļ▓ĢņØĆ column-prefix ņĢĢņČĢ ļ░®ņŗØņØä ņØ┤ņÜ®ĒĢśņŚ¼, data-dictionaryļØ╝ļŖö Ļ▓āņØä ņØ┤ņÜ®ĒĢśņŚ¼ ņĢĢņČĢ ĒÜ©ņ£©ņä▒ņØä ļŹö ļåÆņØ╝ ņłś ņ׳ļŖö ļ░®ļ▓ĢņØ┤ļŗż. Data-dictionaryļŖö Anchor-record ļ░öļĪ£ ļÆżņŚÉ ļ¦īļōżņ¢┤ņ¦äļŗż.
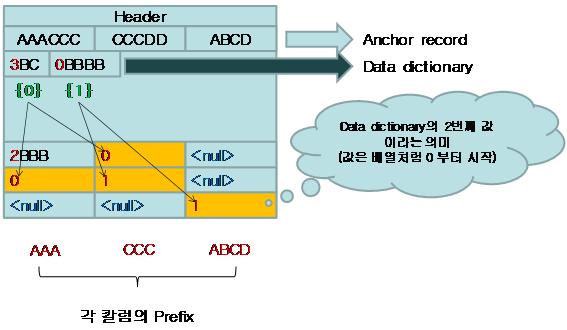
[edit]
4 Overhead #
CPU ņśżļ▓äĒŚżļō£Ļ░Ć ņ׳ļŗż. ļŹ░ņØ┤Ēä░ņŚÉ ļö░ļØ╝ņä£ ņĢĢņČĢļźĀņØ┤ ņóŗņ¦Ć ļ¬╗ ĒĢśĻ│Ā, CPU ņé¼ņÜ®ļ¤ēļ¦ī ņ”ØĻ░Ć ĒĢĀ ņłś ņ׳ņ£╝ļ»ĆļĪ£ Compression/De-Compression ņŚÉ ļīĆĒĢ£ ĒģīņŖżĒŖĖļÅä ĒĢäņÜöĒĢśļŗż.
[edit]
5 ņśłņĀ£ #
ņĢĢņČĢļźĀ ņĪ░ĒÜī
EXEC sp_estimate_data_compression_savings 'ņŖżĒéżļ¦ł','ĒģīņØ┤ļĖö',NULL, NULL, 'PAGE' EXEC sp_estimate_data_compression_savings 'ņŖżĒéżļ¦ł','ĒģīņØ┤ļĖö', NULL, NULL, 'ROW'
ļÅÖņĀüĻ┤Ćļ”¼ĒĢ©ņłś
sys.dm_db_index_physical_stats ļź╝ ņé¼ņÜ®ĒĢśņŚ¼ ļ¼╝ļ”¼ņĀüņØĖ ņĀĢļ│┤ļź╝ ņ¢╗ļŖöļŗż.
sys.dm_db_index_physical_stats ļź╝ ņé¼ņÜ®ĒĢśņŚ¼ ļ¼╝ļ”¼ņĀüņØĖ ņĀĢļ│┤ļź╝ ņ¢╗ļŖöļŗż.
ņŗżņĀ£ ņśłņĀ£
USE AdventureWorks2008;
GO
IF OBJECT_ID('dbo.temp') IS NOT NULL
DROP TABLE dbo.temp;
GO
SELECT A.*
INTO dbo.temp
FROM HumanResources.Employee a, HumanResources.Employee b, HumanResources.Employee c
GO
EXEC sp_spaceused 'dbo.temp';
/*
rows : 24389000
reserved: 4386456 KB
data : 4386392 KB
*/
ALTER TABLE temp
REBUILD
WITH (DATA_COMPRESSION = PAGE)
GO
EXEC sp_spaceused 'dbo.temp';
/*
rows : 24389000
reserved: 297616 KB
data : 297432 KB
*/
[edit]
6 ĒģīņØ┤ļĖö ļ░Å ņØĖļŹ▒ņŖż, ĒĢäĒä░ļ¦üļÉ£ ņØĖļŹ▒ņŖżņŚÉ ļīĆĒĢ£ ņĢĢņČĢ ņśłņĀ£ #
alter table ņŖżĒéżļ¦łļ¬ģ.ĒģīņØ┤ļĖöļ¬ģ rebuild with (data_compression = row); alter table ņŖżĒéżļ¦łļ¬ģ.ĒģīņØ┤ļĖöļ¬ģ rebuild with (data_compression = page); alter index ņØĖļŹ▒ņŖżļ¬ģ on ņŖżĒéżļ¦łļ¬ģ.ĒģīņØ┤ļĖöļ¬ģ rebuild with (data_compression = page); alter index ņØĖļŹ▒ņŖżļ¬ģ on ņŖżĒéżļ¦łļ¬ģ.ĒģīņØ┤ļĖöļ¬ģ rebuild with (data_compression = row); create index ņØĖļŹ▒ņŖżļ¬ģ on ņŖżĒéżļ¦łļ¬ģ.ĒģīņØ┤ļĖöļ¬ģ (producttype, productkey) where ņ╗¼ļ¤╝ļ¬ģ in (1,2) with (data_compression = page);
[edit]
7 DBņØś ļ¬©ļōĀ ĒģīņØ┤ļĖö ļ░Å ņØĖļŹ▒ņŖż ņĢĢņČĢĒĢśĻĖ░ #
ĻĖ░ļ│ĖņĀüņ£╝ļĪ£ page ņĢĢņČĢņØä ĒĢśļ®░, ĒĢäņÜöņŚÉ ļö░ļØ╝ņä£ row ņĢĢņČĢņ£╝ļĪ£ ņłśņĀĢĒĢśļÅäļĪØ ĒĢśņé╝..ļ¬©ļŗłĒä░ļ¦üņØĆ ļŗżļźĖ ņäĖņģśņŚÉņä£ tempdb.dbo.[5E47F809-DACB-4918-B9EC-14CD495E3B3A] ĒģīņØ┤ļĖöņØä ņĪ░ĒÜīĒĢśņé╝.. ņĢĢņČĢ ņĢłĒĢ£ ņØĖļŹ▒ņŖż ļ░Å ĒģīņØ┤ļĖöļ¦ī ņĢĢņČĢĒĢ£ļŗż.
set statistics io off
set nocount on
if object_id('tempdb.dbo.[5E47F809-DACB-4918-B9EC-14CD495E3B3A]') is not null
drop table tempdb.dbo.[5E47F809-DACB-4918-B9EC-14CD495E3B3A]
create table tempdb.dbo.[5E47F809-DACB-4918-B9EC-14CD495E3B3A]
(
sql_str varchar(1000)
);
declare @tname varchar(500);
declare cur cursor for
select query
from (
select
'alter table ' + table_schema + '.' + table_name +
' rebuild with (data_compression = page, online=on)' query
, (select top 1 data_compression_desc
from sys.partitions
where object_id = object_id(table_schema + '.' + table_name)
and index_id = 0) compress --heap
from information_schema.tables
where table_name <> 'sysdiagrams'
and table_type = 'BASE TABLE'
union all
select
'alter index ' + b.name + ' on ' +
schema_name(a.uid) + '.' + a.name +
' rebuild with (data_compression = page, online=on)'
, (select top 1 data_compression_desc
from sys.partitions
where object_id = object_id(table_schema + '.' + table_name)
and rows >= 1000000 -- 1ļ░▒ļ¦ī Ļ▒┤ ņØ┤ņāüļ¦ī..
and index_id = b.index_id) compress
from sys.sysobjects a
inner join sys.indexes b
on a.id = b.object_id
inner join information_schema.tables c
on schema_name(a.uid) + '.' + a.name = table_schema + '.' + table_name
where c.table_name <> 'sysdiagrams'
and c.table_type = 'BASE TABLE'
and b.name is not null
) t
where compress = 'NONE' --ņĢĢņČĢĒĢ£Ļ▒░ļŖö ņĀ£ņÖĖĒĢśĻ│Ā, ņĢĢņČĢ ņĢłĒĢ£Ļ▒░ļ¦ī ņĢĢņČĢĒĢ£ļŗż.. ļ¦ÉņØ┤ ņÜ░ļü╝ļäż..
open cur;
fetch next from cur into @tname;
while @@FETCH_STATUS not in (-1, -2)
begin
--exec(@tname);
print @tname;
insert tempdb.dbo.[5E47F809-DACB-4918-B9EC-14CD495E3B3A] values(@tname);
fetch next from cur into @tname;
end
close cur;
deallocate cur;
if object_id('tempdb.dbo.[5E47F809-DACB-4918-B9EC-14CD495E3B3A]') is not null
drop table tempdb.dbo.[5E47F809-DACB-4918-B9EC-14CD495E3B3A]
[edit]
8 ņĢĢņČĢņŚ¼ļČĆ ņĪ░ĒÜī #
ĒīīĒŗ░ņģśņŚÉ ļīĆĒĢ£ ņĀĢļ│┤ļŖö ĒģīņØ┤ļĖöņØś ņØĖļŹ▒ņŖż ļ░Å ĒīīĒŗ░ņģś ņĀĢļ│┤ļ│┤ĻĖ░ ļ¼Ėņä£ļź╝ ņ░ĖĻ│ĀĒĢśļØ╝.
select * --data_compression_desc ņ╗¼ļ¤╝ ņ░ĖĻ│Ā
from sys.partitions
where object_id = object_id('dbo.aaa')
drop table if exists #temp
select
concat(schema_name(schema_id), '.', name) table_name
, b.compression_cnt
, b.none_cnt
, b.rows
into #temp
from sys.objects a
cross apply (
select
count(case when data_compression_desc = 'NONE' then 1 end) none_cnt
, count(case when data_compression_desc <> 'NONE' then 1 end) compression_cnt
, sum(rows) rows
from sys.partitions
where object_id = a.object_id
) b
where a.type = 'u'
select * from #temp order by 1
[edit]
9 ĒīīĒŗ░ņģś ņĢĢņČĢ #
ĻĖ░ļ│ĖņĀüņ£╝ļĪ£ ļŗżņØīĻ│╝ Ļ░ÖņØ┤ ĒĢ£ļŗż.
ALTER TABLE PartitionTable1 REBUILD PARTITION = ALL WITH (DATA_COMPRESSION = PAGE ON PARTITIONS(1) ) ; GO ALTER TABLE PartitionTable1 REBUILD PARTITION = ALL WITH ( DATA_COMPRESSION = PAGE ON PARTITIONS(1), DATA_COMPRESSION = ROW ON PARTITIONS(2 TO 4) ) ; GO
ņŖżĒü¼ļ”ĮĒŖĖļÅä ļ¦īļōżņ¢┤ ļ│┤ņĢśļŗż. ņĢäļלļŖö ĒģīņØ┤ļĖö ņĢĢņČĢ.
set nocount on
set statistics io off
declare
@bdt char(8)
, @edt char(8)
, @p int
, @sql varchar(4000)
set @bdt = '20110928'
while (@bdt <= '20300301')
begin
set @edt = convert(char(8), dateadd(dd, 1, @bdt), 112)
set @p = $partition.ĒīīĒŗ░ņģśĒĢ©ņłś(@bdt)
set @sql = '
alter table ĒģīņØ┤ļĖöļ¬ģ
rebuild partition = ' + convert(varchar, @p) + '
with (data_compression = page)'
--exec (@sql)
print @sql
--print @bdt + ', ' + @edt
set @bdt = @edt
end
ņØĖļŹ▒ņŖż ņĢĢņČĢ
set nocount on
set statistics io off
declare
@bdt char(8)
, @edt char(8)
, @p int
, @sql varchar(4000)
set @bdt = '20111123'
while (@bdt <= '20121027')
begin
set @edt = convert(char(8), dateadd(dd, 1, @bdt), 112)
set @p = $partition.ĒīīĒŗ░ņģśĒĢ©ņłś(@bdt)
set @sql = '
alter index ņØĖļŹ▒ņŖżļ¬ģ
on ņŖżĒéżļ¦łļ¬ģ.ĒģīņØ┤ļĖöļ¬ģ
rebuild partition = ' + convert(varchar, @p) + '
with (data_compression = page)'
--exec (@sql)
print @sql
--print @bdt + ', ' + @edt
set @bdt = @edt
end
[edit]
10 Ļ▓░ļĪĀ #
ĒĢäņ×ÉņØś ĒģīņŖżĒŖĖĻ▓░Ļ│╝ ņØ╝ļ░śņĀüņ£╝ļĪ£ page ņĢĢņČĢņØ┤ ņóĆ ļŹö ņĢĢņČĢņØ┤ ņל ļÉśņŚłļŗż. ņĢĢņČĢņØä ņ¢┤ļ¢╗Ļ▓ī ĒĢśļŖöņ¦ĆļÅä ņäżļ¬ģĒ¢łļŗż. ļŁÉ.. ņØ┤ļ¤░Ļ▒░ ņĢīļ®┤ ļŁÉĻ░Ć ļŗ¼ļØ╝ņ¦Ćļéś? ļé┤Ļ░Ć ņĢĢņČĢ ļ░®ļ▓ĢņØä ļ░öĻ┐Ć ņłśļÅä ņŚåļŖöļŹ░ ļ¦ÉņØ┤ļŗż. ņĢäļ¼┤ļלļÅä ņ×Ŗņ¢┤ļ▓äļ”¼ļŖöĻ▓ī ļŹö ļé½Ļ▓īļŗżļŖö ņāØĻ░üņØä ĒĢ┤ļ│Ėļŗż.
ļŹ░ņØ┤Ēä░ ņżæļ│ĄņŚÉ ņØśĒĢ£ ņä▒ļŖź ļ¼ĖņĀ£ļź╝ ĒĢ┤Ļ▓░ĒĢśĻĖ░ ņ£äĒĢ£ ļ░®ļ▓Ģ ņżæņŚÉ ņøÉņ▓£ņĀüņØĖ ĒĢ┤Ļ▓░ļ░®ļ▓Ģņ£╝ļĪ£ ņĀĢĻĘ£ĒÖöĻ░Ć ņ׳ļŗż. ņŚ¼ņØśņ╣ś ņĢŖļŗżļ®┤ ņØ┤ļ¤░ ņĢĢņČĢĻĖ░ņłĀņØ┤ļéś ĒĢśļō£ņø©ņ¢┤ņŚÉņä£ ņ¦üņĀæņĀüņ£╝ļĪ£ ņĀ£Ļ│ĄĒĢśļŖö ļŹ░ņØ┤Ēä░ ņżæļ│Ą ņĀ£Ļ▒░ ĻĖ░ņłĀņØä ņØ┤ņÜ®ĒĢśļ®┤ ļÉĀ Ļ▓āņØ┤ļŗż. ņØ┤ļ¤¼ĒĢ£ ņåöļŻ©ņģśņØĆ ņé¼ļ×īņØä 1ļ¬ģ ļŹö ļĮæļŖöĻ▒░ ļ│┤ļŗż ņ¢┤ņ®īļ®┤ ļŹö ĒÜ©ņ£©ņĀüņØ╝ ņłśļÅä ņ׳ļŗż..
[edit]
11 ņ░ĖĻ│Āņ×ÉļŻī #
ņ░ĖĻ│Āņ×ÉļŻīļź╝ ņÜöņĢĮĒĢśļ®┤ 3ļ░▒ ļ¦ī Ļ▒┤ņØś Ļ│ĀĻ░Ø ĒģīņØ┤ļĖöņØä ĒÆĆņŖżņ║öĒĢśļŖöļŹ░ 52ņ┤ł Ļ▒Ėļ”¼ļŖöļŹ░, ņĢĢņČĢņØä Ē¢łļŹöļŗł 3ņ┤łļ¦īņŚÉ ļüØļé¼ļŗż. ņĢĢņČĢņØä ĒĢśņ¦Ć ņĢŖņĢśņØä ļĢīļŖö 2263 Pageļź╝ ņØĮņŚłĻ│Ā, ņĢĢņČĢņØä Ē¢łņØä ļĢīļŖö 534 Pageļź╝ ņØĮņŚłļŗż. (ņĢä.. ĒģīņŖżĒŖĖ ĒĢśļō£ņø©ņ¢┤ ņĪ░ļéĖ ĻŠĖņĪīļäż.. 2263 pageļź╝ 52ņ┤ł? ŃģĪŃģĪ;;)
![[http]](/moniwiki/imgs/http.png) Data Compression: Strategy, Capacity Planning and Best Practices
Data Compression: Strategy, Capacity Planning and Best Practices
![[http]](/moniwiki/imgs/http.png) Row compression in SQL Server 2008
Row compression in SQL Server 2008
![[http]](/moniwiki/imgs/http.png) Page compression in SQL Server 2008
Page compression in SQL Server 2008
![[http]](/moniwiki/imgs/http.png) A Unicode Compression example
A Unicode Compression example
![[http]](/moniwiki/imgs/http.png) Unicode Compression in SQL Server 2008R2
Unicode Compression in SQL Server 2008R2
![[http]](/moniwiki/imgs/http.png) Customer feedback on Data Compression
Customer feedback on Data Compression
![[http]](/moniwiki/imgs/http.png) Update on data compression performance/space-savings and links to published white papers
Update on data compression performance/space-savings and links to published white papers
’╗┐